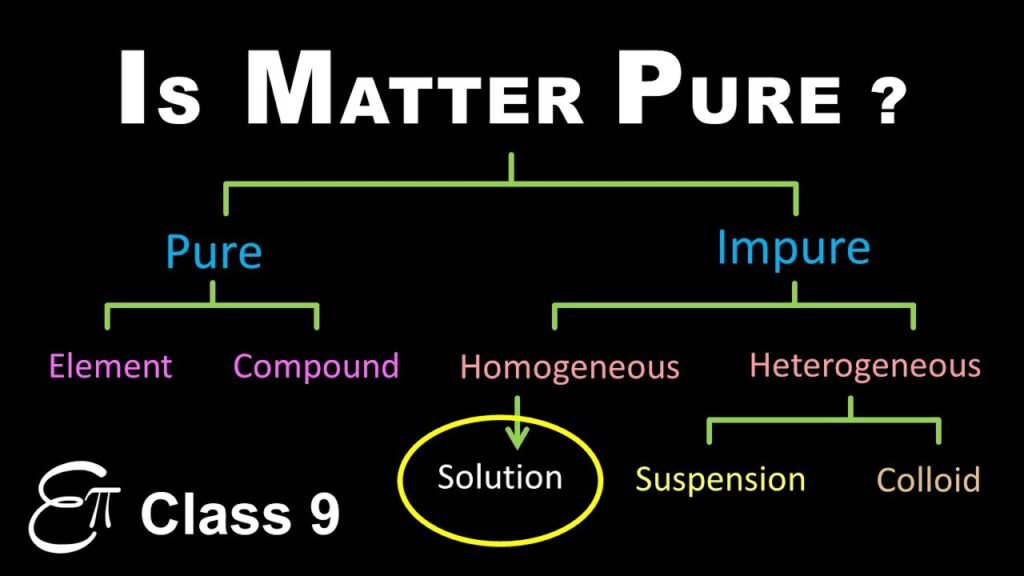
📘 Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
🔹 1. Pure Substance
- Contains only one type of particle.
- Fixed composition and properties.
- Examples: Distilled water, oxygen, gold.
🔹 2. Mixture
- Contains two or more substances mixed physically.
- Can be separated by physical methods.
- Composition is not fixed.
- Examples: Air, milk, soil.
🔹 3. Types of Mixtures
a) Homogeneous Mixture
- Uniform throughout.
- Components evenly mixed.
- Examples: Salt in water, air.
b) Heterogeneous Mixture
- Non-uniform; parts visible.
- Examples: Soil, sand in water.
🔹 4. Based on Particle Size
| Type | Appearance | Particle Size | Tyndall Effect | Settle Down |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution | Clear | Small | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Suspension | Cloudy | Large | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Colloid | Looks uniform | Medium | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
🔹 5. Solution
- Homogeneous mixture of solute + solvent.
- Particles do not settle and pass through filter paper.
- Examples: Sugar water, lemonade.
🔹 6. Suspension
- Heterogeneous mixture with large particles.
- Particles settle on standing; scatters light.
- Example: Muddy water.
🔹 7. Colloid
- Intermediate mixture; particles do not settle.
- Shows Tyndall effect.
- Examples: Milk, fog, smoke.
🔹 8. Tyndall Effect
- Light scattering due to colloid/suspension particles.
- Not seen in true solutions.
🔹 9. Alloy
- Homogeneous mixture of metals (or metal + non-metal).
- Examples: Brass (Cu + Zn), Steel (Fe + C).
- Alloys are mixtures, not pure substances.
✅ Practice Questions
A. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Which is a homogeneous mixture?
a) Sand + salt
b) Soil
c) Sugar solution
d) Ice - Method for separating dyes in ink?
a) Filtration
b) Chromatography
c) Sublimation
d) Distillation - Which is a colloid?
a) Salt solution
b) Air
c) Milk
d) Soil - Tyndall effect is shown by:
a) Solution
b) Suspension
c) Colloid
d) Both b and c - Which mixture settles?
a) Solution
b) Suspension
c) Colloid
d) None
B. Assertion & Reason
- A: Milk is a colloid.
R: Colloids scatter light and do not settle. - A: Salt can be separated by filtration.
R: Salt does not dissolve in water. - A: Alloys are mixtures.
R: Made by physically mixing metals. - A: Air is a pure substance.
R: Contains only oxygen molecules. - A: Suspension scatters light.
R: Particles are large and visible.
C. Case-Based Study
Rina had sand + salt. She added water and filtered it.
11.1. What dissolved?
a) Sand b) Salt c) Both d) None
11.2. What remained on filter paper?
a) Salt b) Sand c) Water d) Sugar
11.3. How can Rina recover salt?
a) Decantation
b) Evaporation
c) Filtration
d) Distillation
D. Reason-Based Questions (with Answers)
- Why is muddy water a suspension?
– Because its large particles settle on standing. - Why is milk a colloid?
– Because its fat particles scatter light and do not settle. - Why can’t sugar be separated by filtration?
– Because sugar is completely dissolved and passes through the filter. - Why do colloids scatter light?
– Because their particle size is large enough to scatter light (Tyndall effect).
📌 Answer Key
MCQs:
1–c, 2–b, 3–c, 4–d, 5–b
Assertion & Reason:
6–A: True, R: True (Correct)
7–A: False, R: False
8–A: True, R: True (Correct)
9–A: False, R: False
10–A: True, R: True (Correct)
Case-Based:
11.1–b, 11.2–b, 11.3–b